Influence of tillage and residue-management practices and organic nutrition on performance of soybean (Glycine max) under conservation agriculture in semiarid ecology of India Verma Gaurav1, Dhaka A.K.2,*, Singh Bhagat3, Prakash Ram4, Shabnam5 1Ph.D. Scholar, Department of Agronomy, Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar, 125 004 2Assistant Professor, Department of Agronomy, Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar, 125 004 3Assistant Agronomist, Wheat and Barley Section Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar, 125 004 4Assistant Scientist, Department of Soil Science, Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar, 125 004 5Ph.D. Scholar, Department of Soil Science, Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar, 125 004 *Corresponding author's Email: dhakaanilkumar@yahoo.in
Online published on 29 November, 2023. Abstract A field experiment was conducted during the rainy (kharif) season of 2020 and 2021 at the Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar to evaluate the impact of different tillage and residue-management practices (TRMPs) and organic nutrition on performance of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. The experiment was laid out in a split-plot design with 3 replications. The treatment comprised 4 TRMPs in main plots and 5 organic nutrient management practices in subplot. The result showed that, application of zero tillage with residue (ZT + R) resulted in significantly higher number of branches/plant (9.65), pods/plant (69.2), seeds/pod (2.68), grain yield (1.63 t/ha) and gross return (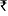 87,480/ha) being statistically at par with conventional tillage with residue (CT + R) and superior to the other treatments. Significantly enhanced yield attributes i.e. branches/plant (9.12), pods/plant (69.8), seeds/pod (2.71) and grain yield (1.6 t/ha) were observed under application of recommended dose of fertilizer (RDF) through inorganic fertilizers followed by recommended dose of nitrogen through vermicompost (VC) + biofertilizer + cow urine (10%) + Panchgavya (5%) + Jeevamrut (500 litres/ha), recommended dose of nitrogen through farmyard manure (FYM) + biofertilizer + cow urine (10% foliar application at vegetative, panicle emergence and flowering stage) + Panchgavya (5% foliar application at vegetative, panicle emergence and flowering stage) + Jeevamrut (500 litres/ha foliar application at 30, 60 and 90 days after sowing (DAS). However, the maximum gross returns realized under N5 ( 87,480/ha) being statistically at par with conventional tillage with residue (CT + R) and superior to the other treatments. Significantly enhanced yield attributes i.e. branches/plant (9.12), pods/plant (69.8), seeds/pod (2.71) and grain yield (1.6 t/ha) were observed under application of recommended dose of fertilizer (RDF) through inorganic fertilizers followed by recommended dose of nitrogen through vermicompost (VC) + biofertilizer + cow urine (10%) + Panchgavya (5%) + Jeevamrut (500 litres/ha), recommended dose of nitrogen through farmyard manure (FYM) + biofertilizer + cow urine (10% foliar application at vegetative, panicle emergence and flowering stage) + Panchgavya (5% foliar application at vegetative, panicle emergence and flowering stage) + Jeevamrut (500 litres/ha foliar application at 30, 60 and 90 days after sowing (DAS). However, the maximum gross returns realized under N5 (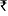 87,280/ha) followed by N4. Hence, combined application of ZT + R along with N5 organic package and followed by ZT + R along with N4 organic package are better options for improving the yield attributes and productivity of soybean crop under conservation agriculture (CA) in semiarid ecology of India and similar agro-eco regions. 87,280/ha) followed by N4. Hence, combined application of ZT + R along with N5 organic package and followed by ZT + R along with N4 organic package are better options for improving the yield attributes and productivity of soybean crop under conservation agriculture (CA) in semiarid ecology of India and similar agro-eco regions. Top Keywords Conservation agriculture, Organic nutrition, Productivity, Tillage practices. Top |